
Investment Casting

Investment Casting
Investment Casting
Investment and precision casting are used to obtain castings with the highest dimensional accuracy, complex geometry and best surface quality. Depending on the material, total quantity and shape of the casting, the appropriate casting process is selected according to economic aspects.
Castings with a mass of 0.001 kg to several kilograms can be produced.
A major advantage of these processes is that the finished cast parts are generally ready for installation. As a rule of thumb, precision casting and investment casting are particularly economical the more complicated the component is designed or the more difficult and costly the post-processing is.
Available materials
- Magnesium alloys
- Aluminum alloys
- Copper alloys
- Iron alloys
- Nickel alloys
- Cobalt alloys
- Other materials on request
Investment Casting
Investment and precision casting are used to obtain castings with the highest dimensional accuracy, complex geometry and best surface quality. Depending on the material, total quantity and shape of the casting, the appropriate casting process is selected according to economic aspects.
Castings with a mass of 0.001 kg to several kilograms can be produced.
A major advantage of these processes is that the finished cast parts are generally ready for installation. As a rule of thumb, precision casting and investment casting are particularly economical the more complicated the component is designed or the more difficult and costly the post-processing is.
Available materials
- Magnesium alloys
- Aluminum alloys
- Copper alloys
- Iron alloys
- Nickel alloys
- Cobalt alloys
- Other materials on request
1. Model production
Flexible or fixed form
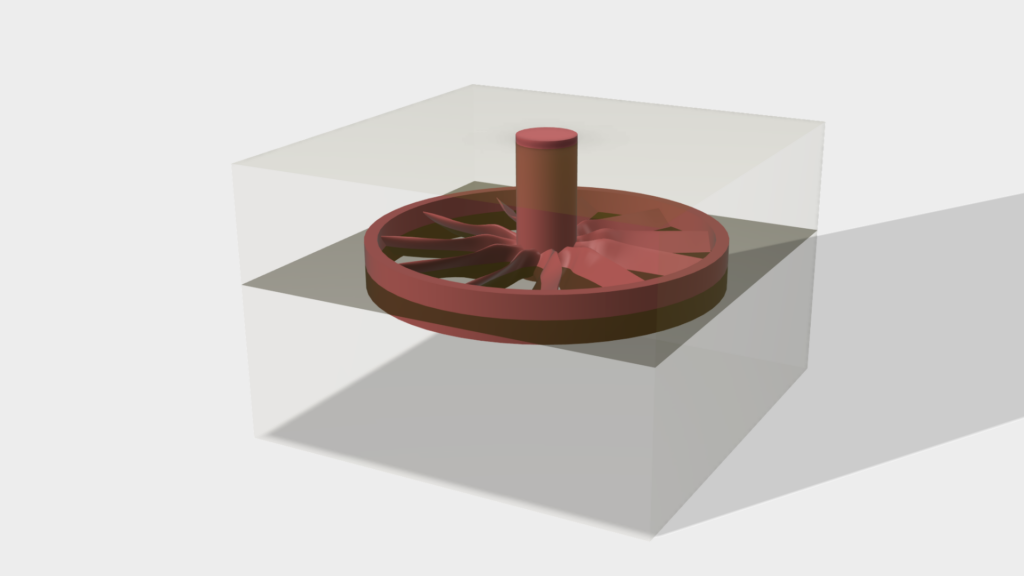
Rapid Prototyping
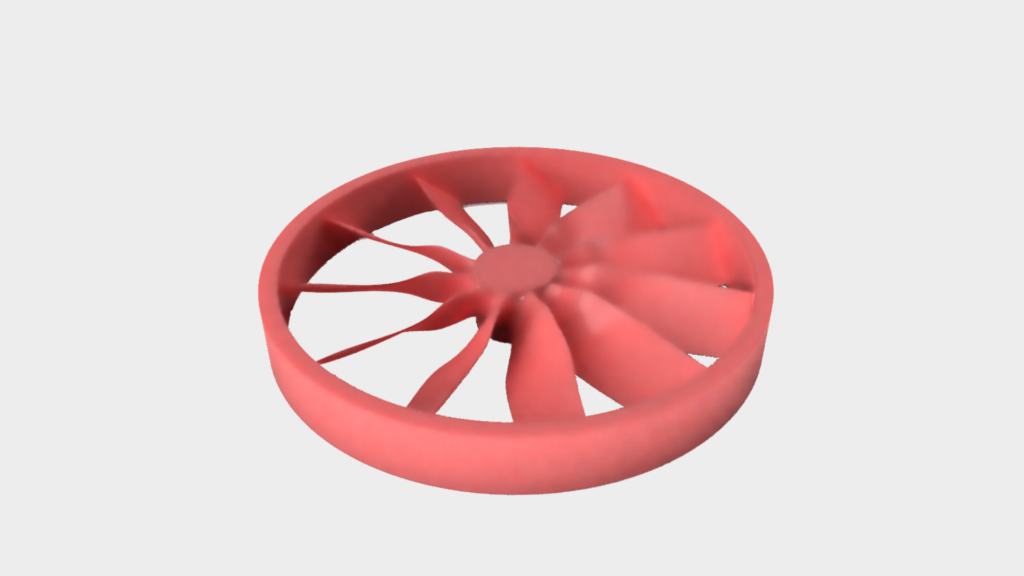
First, a multi-part mold is produced from which wax models of the component to be manufactured are made. To do this, the mold is filled with wax or thermoplastic and the model can be removed from the mold once it has solidified. Alternatively, additive manufacturing can also be used for small series.
2. Assemble the casting cluster
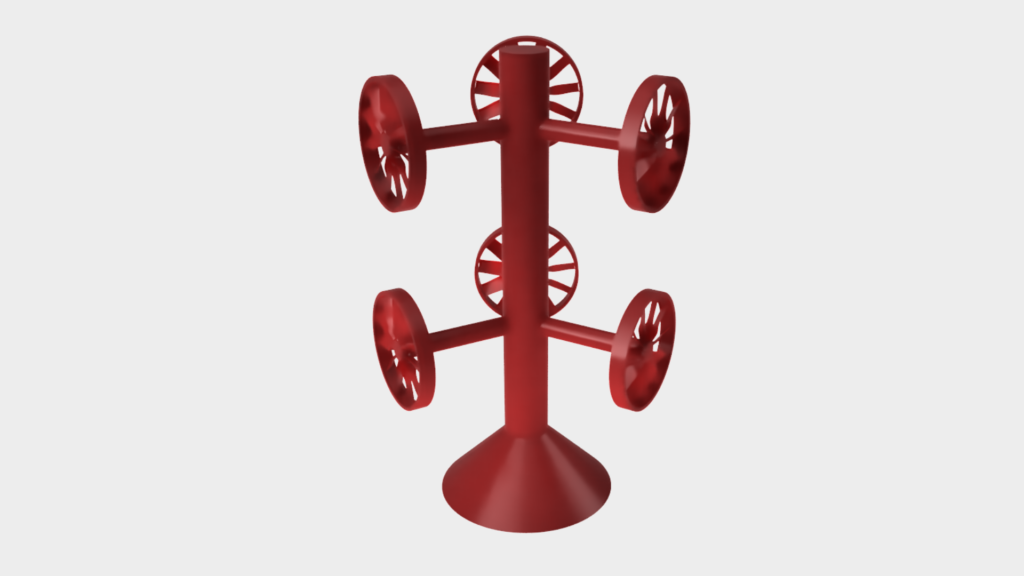

The individual wax models are then assembled into a casting cluster.
3. Produce mold
Dipping and sanding
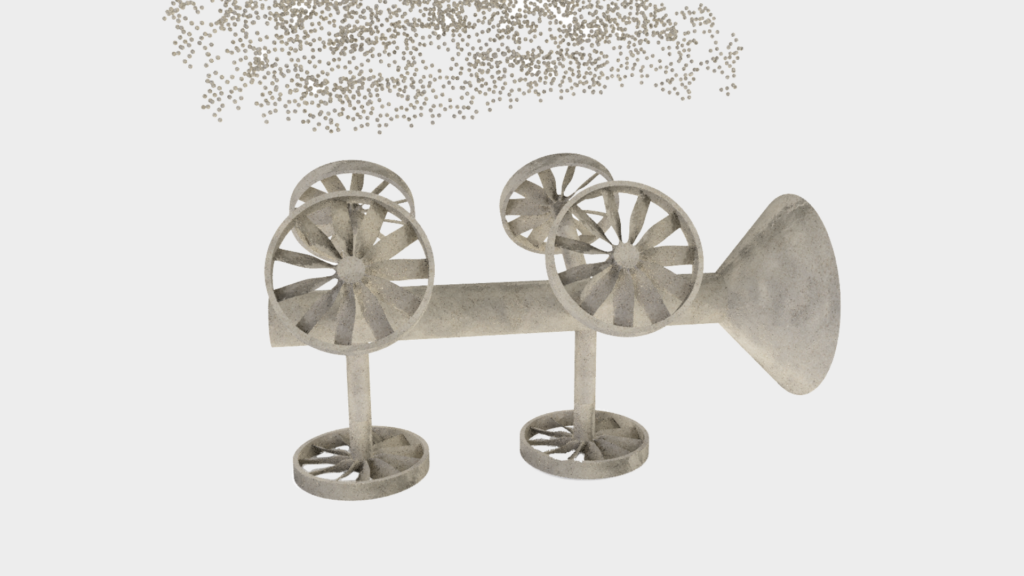

The casting tube is dipped several times in slip and sanded with molding sand. This process is repeated until the desired mask thickness is achieved.
Plaster mold
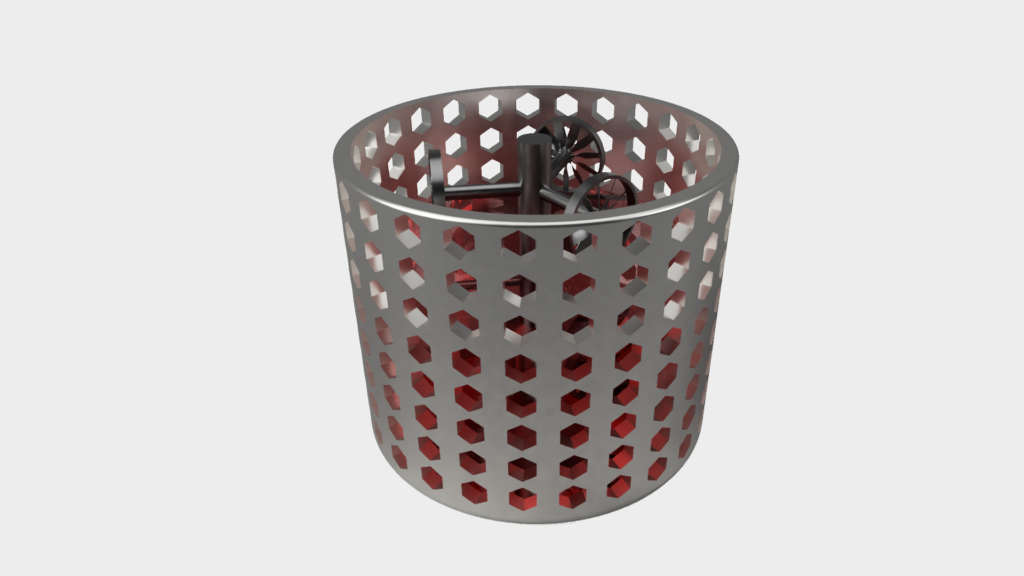

The cast grape is placed in a cuvette and filled with molding material.
4. Melt out wax and burn
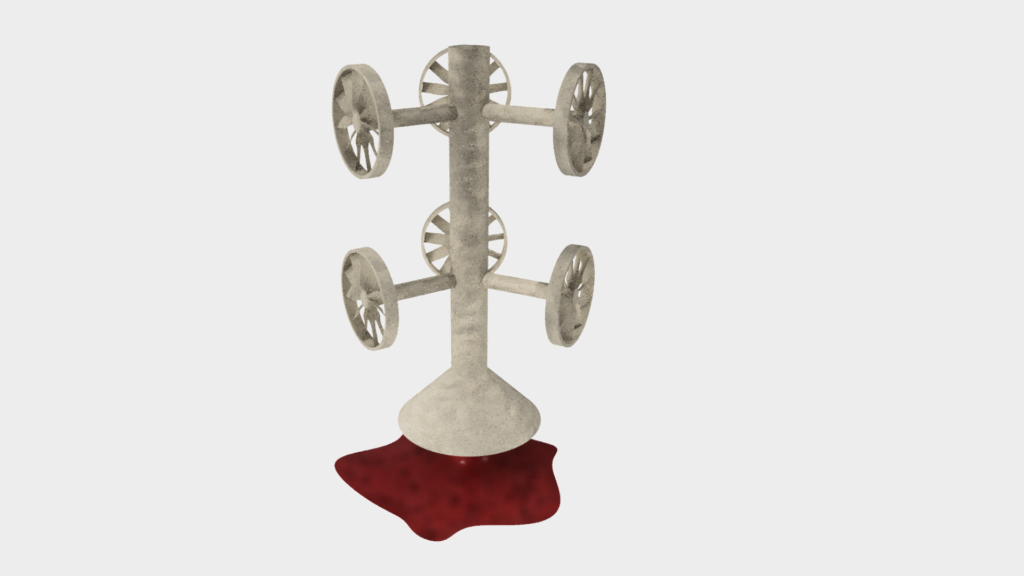

Next, the wax or plastic is melted out and collected to be reused. What remains is a hollow mold.
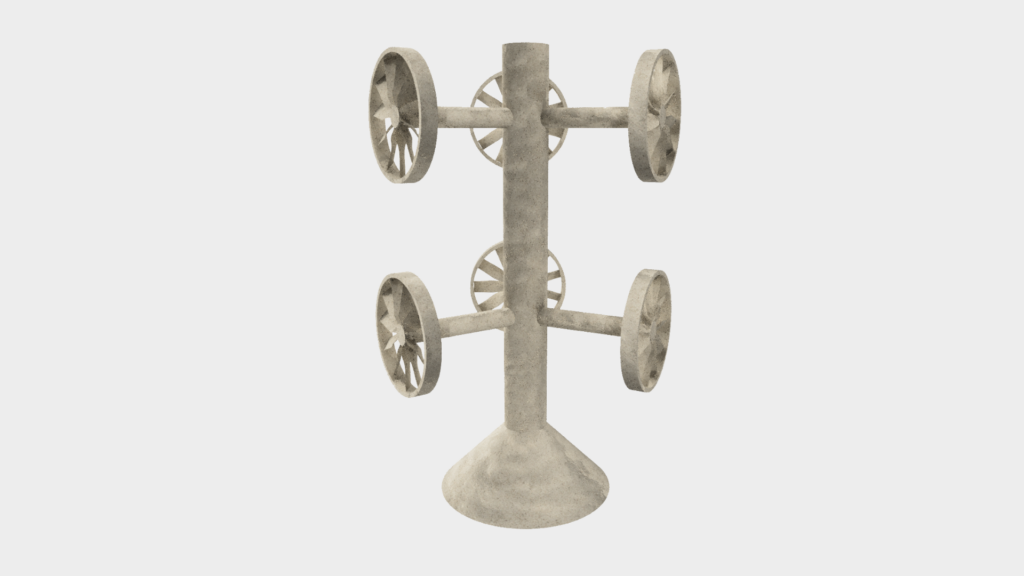

The resulting mold is fired at 800°C, which gives it a ceramic bond.
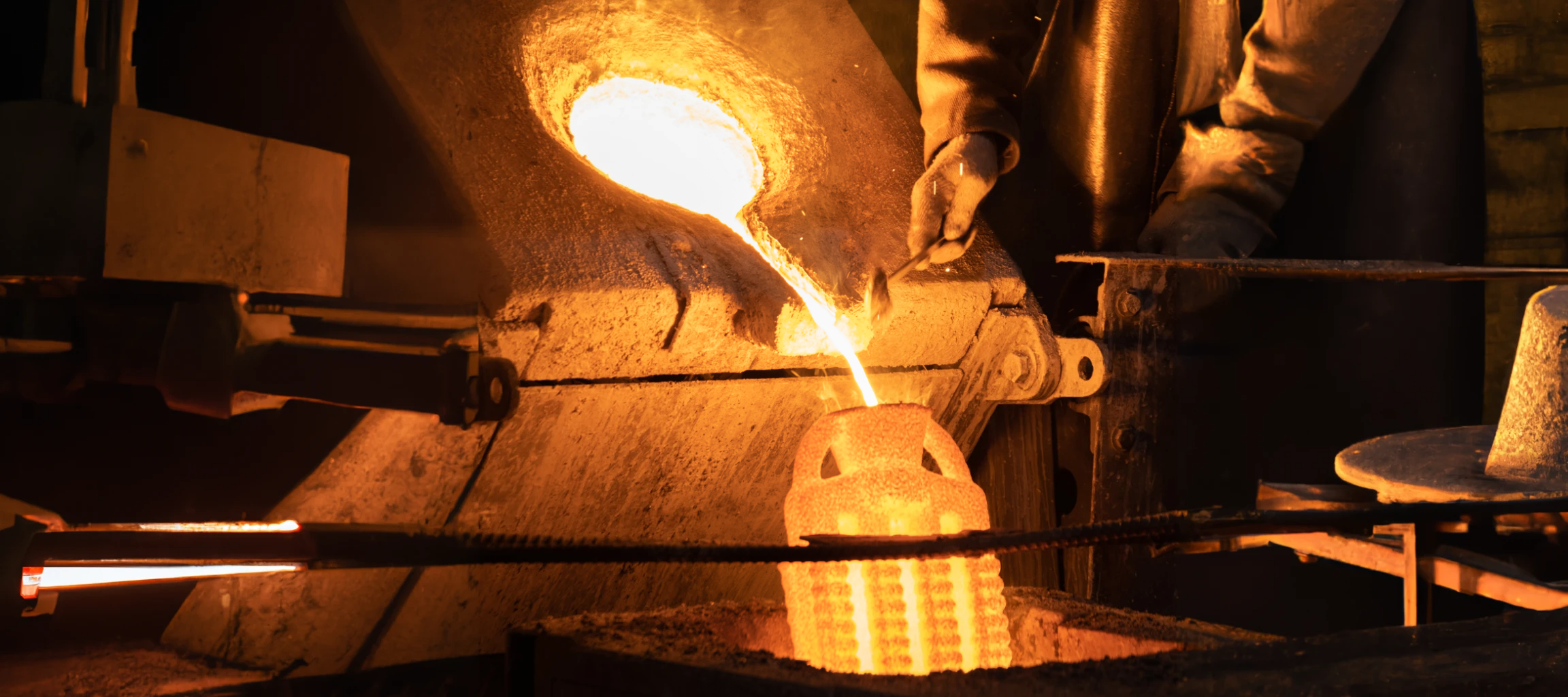
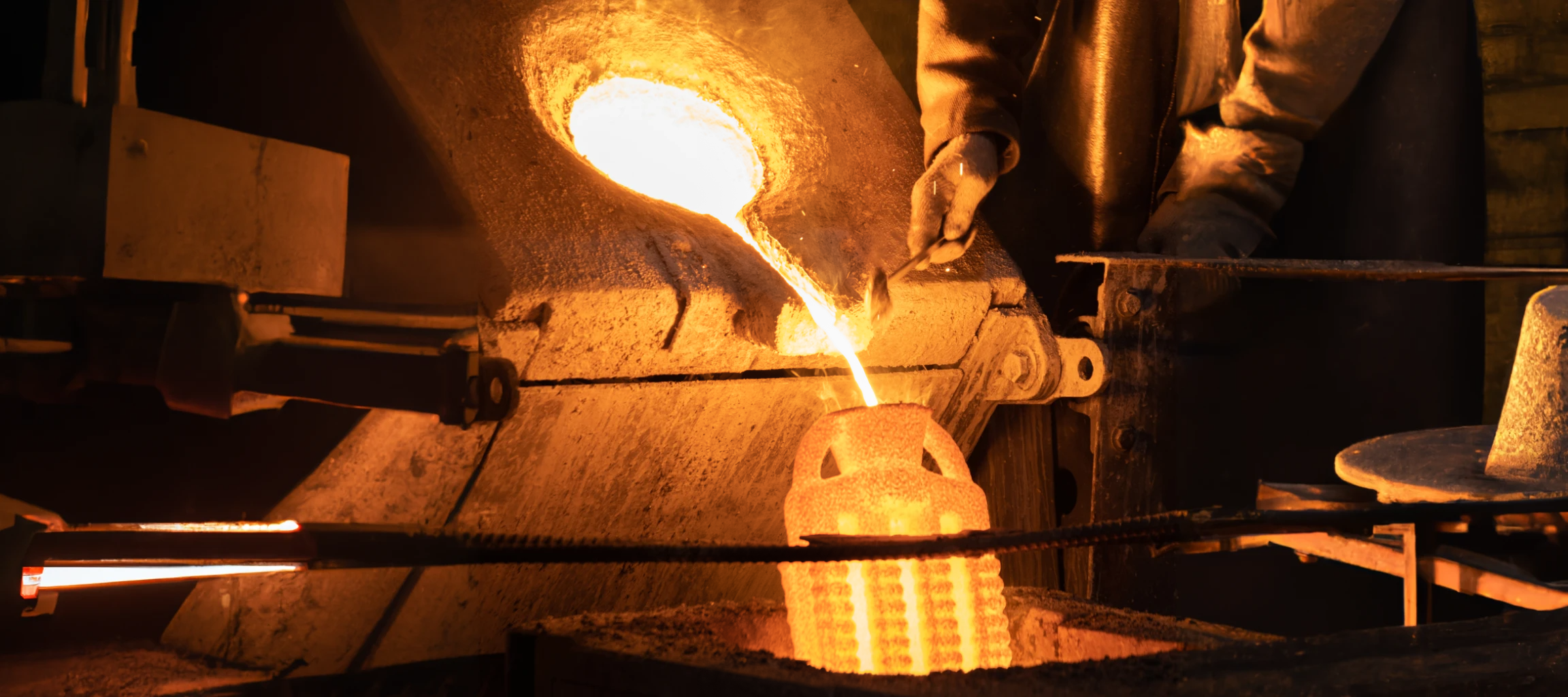
5. Casting
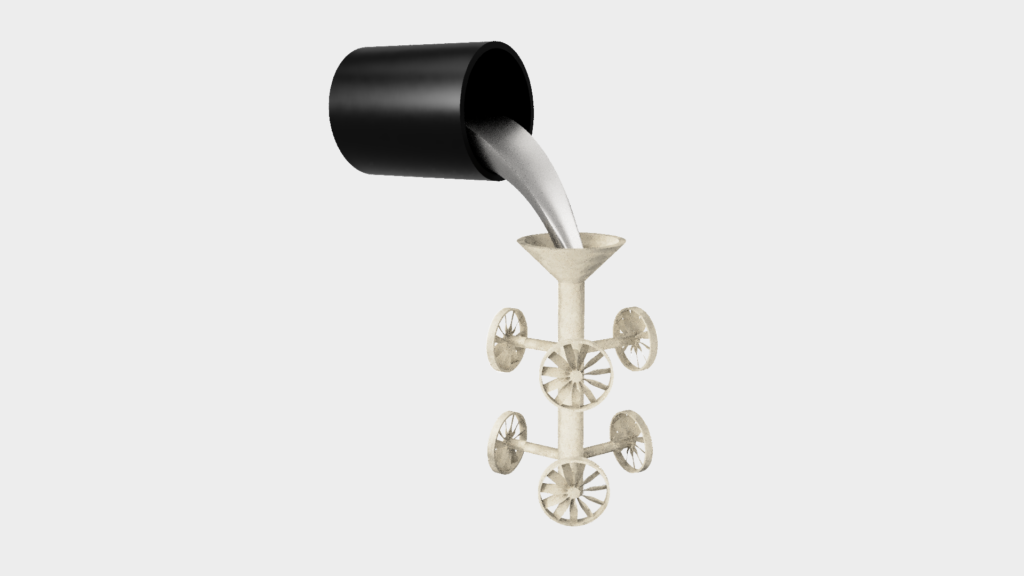

The hollow mold is then filled with molten metal, creating a component with the dimensions of the original model.
6. Demolding
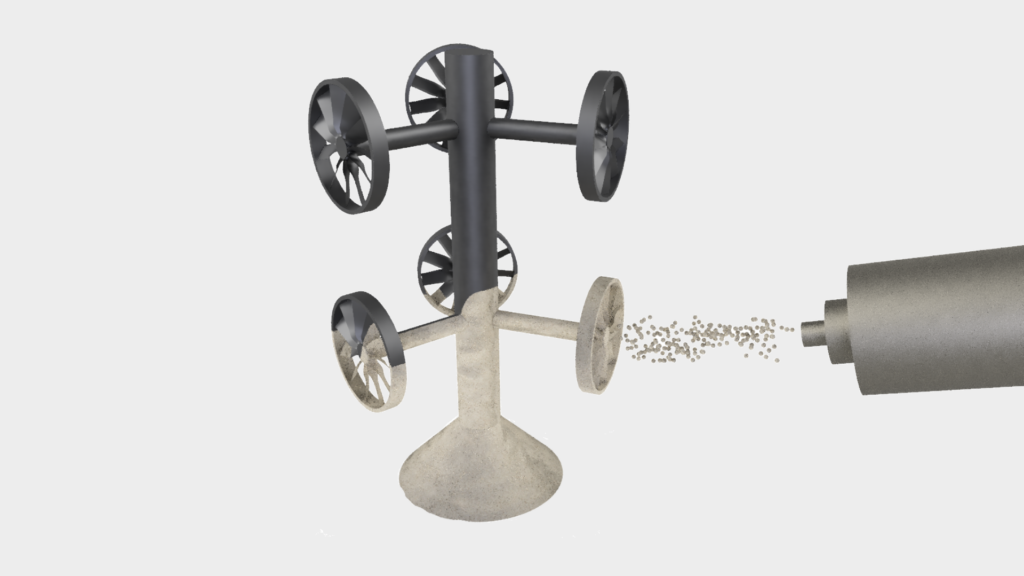

The component is now demolded, destroying the mold. The components are then cleaned by sandblasting several times to remove all mold residue and leave only the clean component.
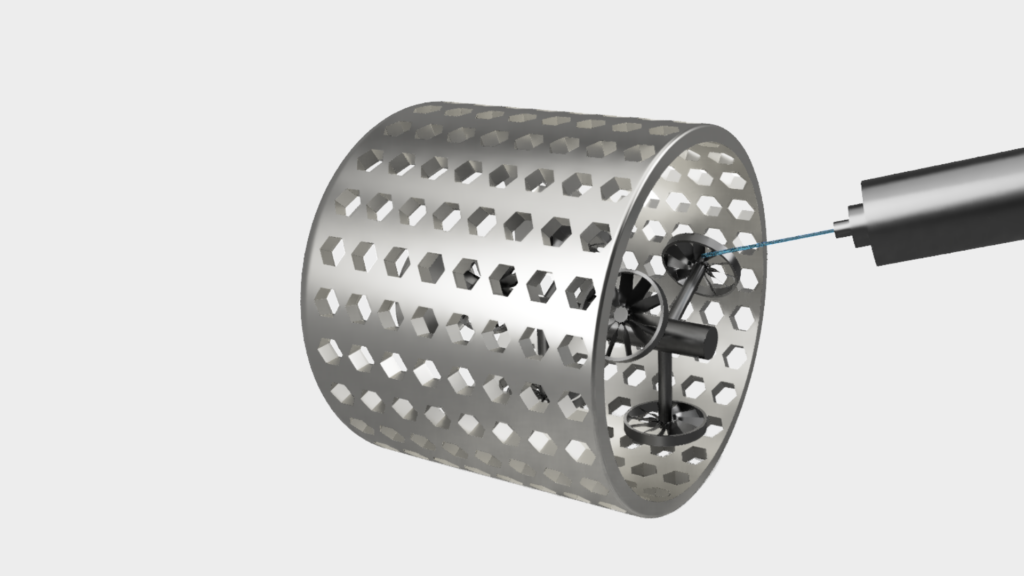
The component is now demolded with the help of water jets.
7. Mechanical pre-machining
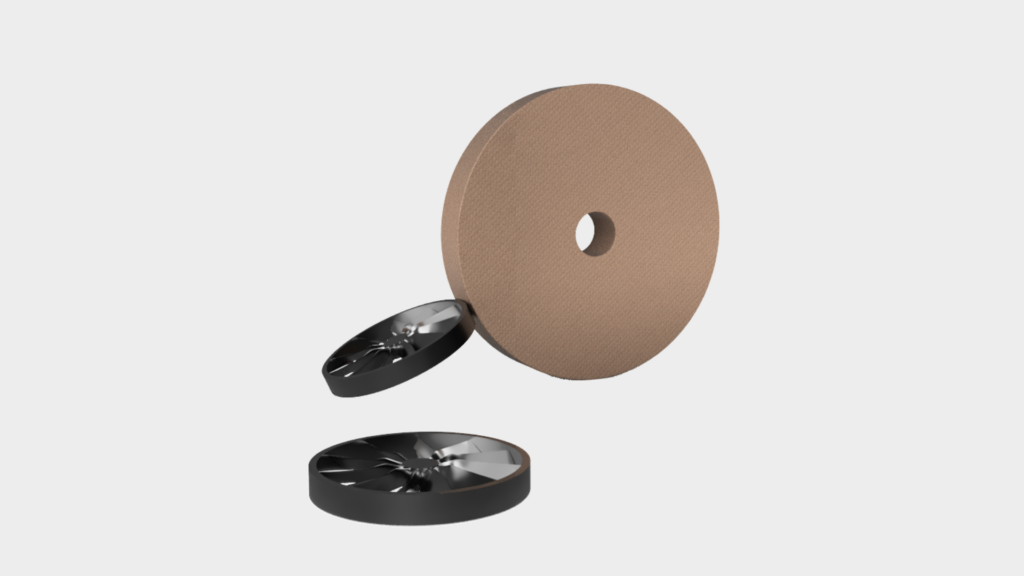

First, the components are sawn off at the original connection point. As the surface still has sprue residues, these must be removed using suitable methods such as grinding or turning.
8. Finishing
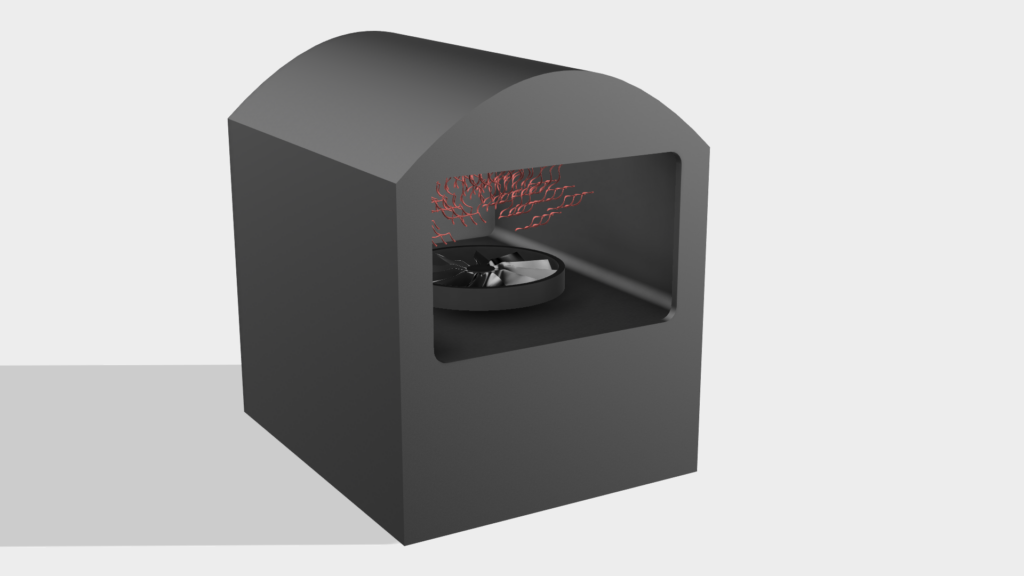
Depending on customer requirements, further processing steps can now be carried out. For example, holes and threads can be drilled, the surface galvanized or heat treated. In this step, the customer’s specific wishes and requirements are implemented.
Drilling, milling, lathing
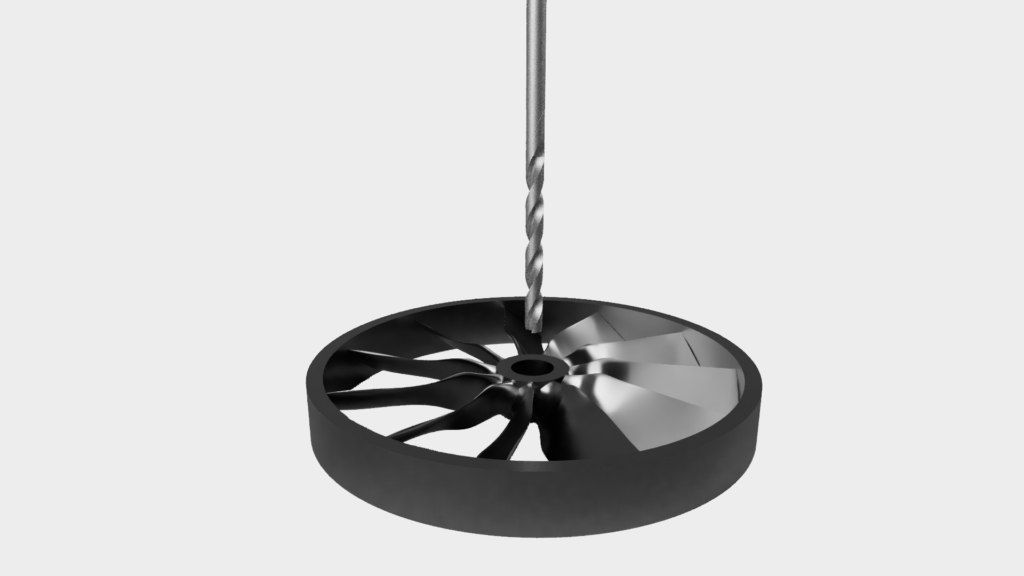

Surface refinement
Heat treatment

9. Quality control
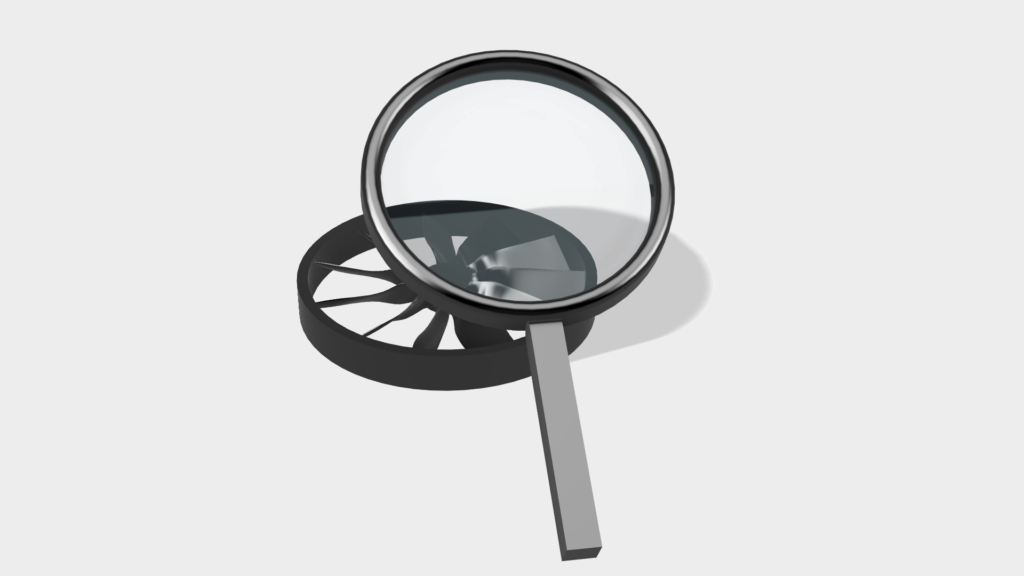

In the final step, the component is subjected to a quality check. It is carefully checked for damage or defects so that all components meet our high quality requirements. This step completes the entire process and the component is ready for use.
1. Model production
Flexible or fixed form

Rapid Prototyping

First, a multi-part mold is produced from which wax models of the component to be manufactured are made. To do this, the mold is filled with wax or thermoplastic and the model can be removed from the mold once it has solidified. Alternatively, additive manufacturing can also be used for small series.
2. Assemble the casting cluster

The individual wax models are then assembled into a casting cluster.
3. Produce mold
Dipping and sanding

The casting tube is dipped several times in slip and sanded with molding sand. This process is repeated until the desired mask thickness is achieved.
Plaster mold

The cast grape is placed in a cuvette and filled with molding material.
4. Melt out wax and burn

Next, the wax or plastic is melted out and collected to be reused. What remains is a hollow mold.

The resulting mold is fired at 800°C, which gives it a ceramic bond.
5. Casting

The hollow mold is then filled with molten metal, creating a component with the dimensions of the original model.
6. Demolding

The component is now demolded, destroying the mold. The components are then cleaned by sandblasting several times to remove all mold residue and leave only the clean component.

The component is now demolded with the help of water jets.
7. Mechanical pre-machining

First, the components are sawn off at the original connection point. As the surface still has sprue residues, these must be removed using suitable methods such as grinding or turning.
8. Finishing
Depending on customer requirements, further processing steps can now be carried out. For example, holes and threads can be drilled, the surface galvanized or heat treated. In this step, the customer’s specific wishes and requirements are implemented.
Drilling, milling, lathing

Surface refinement

Heat treatment

9. Quality control

In the final step, the component is subjected to a quality check. It is carefully checked for damage or defects so that all components meet our high quality requirements. This step completes the entire process and the component is ready for use.
